
Mesoderm vector illustration VectorMine Nursing school notes, Human body anatomy, Physiology
Abstract. The three germ layers — mesoderm, endoderm and ectoderm — constituting the cellular blueprint for the tissues and organs that will form during embryonic development, are specified at gastrulation. Cells of mesodermal origin are the most abundant in the human body, representing a great variety of cell types, including the.

Ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm Diagram Quizlet
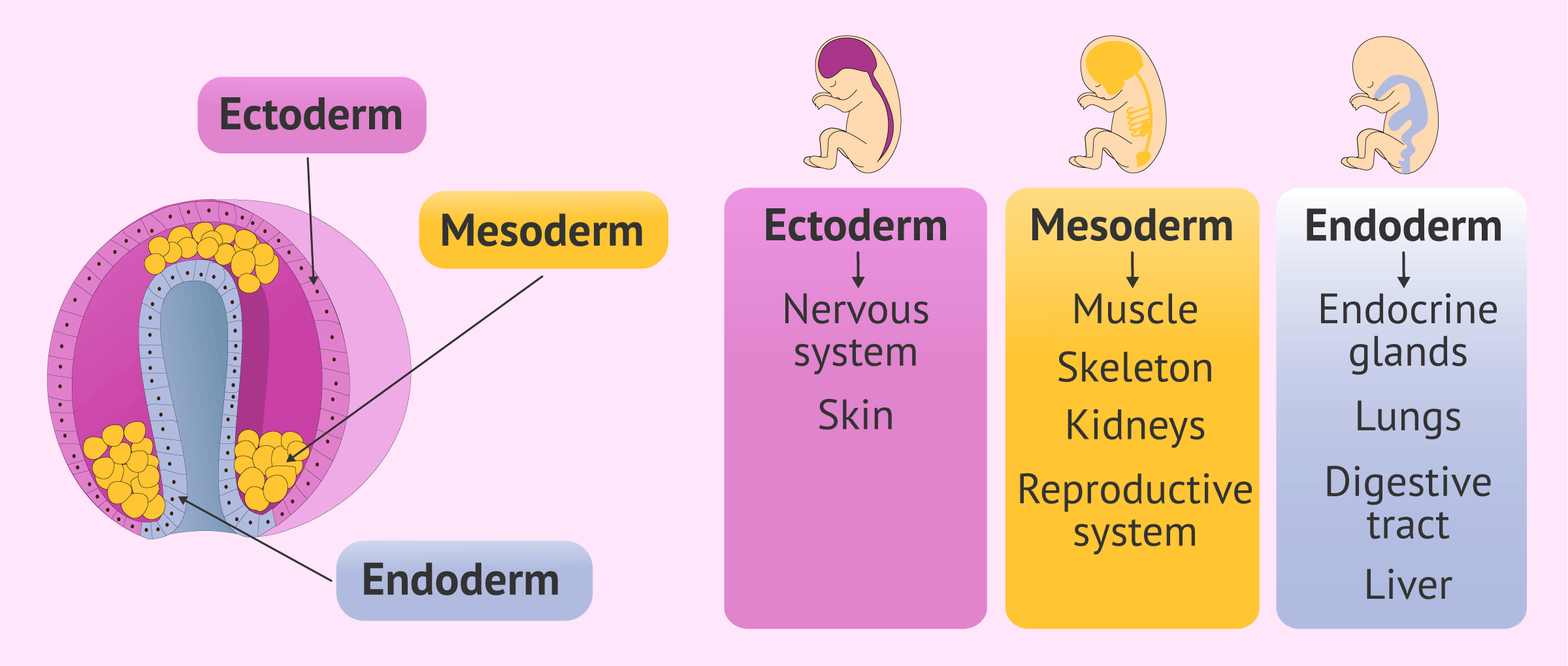
AboutTranscript. Explore the formation of specific structures from the three primary germ layers - endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm - during early embryogenesis. Discover how endoderm cells shape our gastrointestinal and pulmonary systems, mesoderm forms muscles, skeletal system, and genitourinary tracts, and ectoderm creates skin, related.

SOLUTION Anatomy mesoderm ectoderm and endoderm Studypool
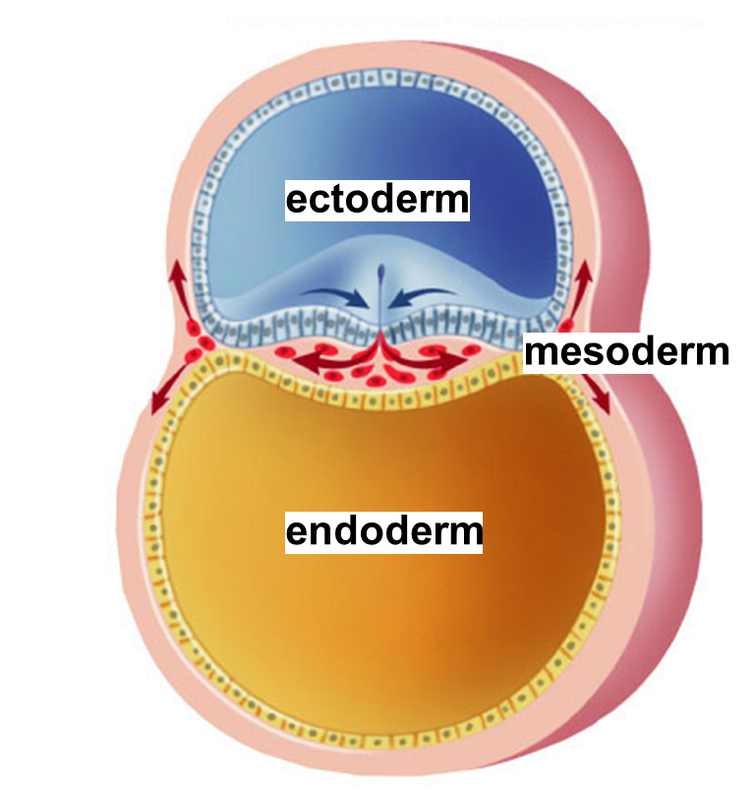
germ layer, any of three primary cell layers, formed in the earliest stages of embryonic development, consisting of the endoderm (inner layer), the ectoderm (outer layer), and the mesoderm (middle layer). The germ layers form during the process of gastrulation, when the hollow ball of cells that constitutes the blastula begins to differentiate.
Reproduction and Development AP biology
The endoderm produced during gastrulation will form the lining of the digestive tract, as well as that of the lungs and thyroid. For animals with three germ layers, after the endoderm and ectoderm have formed, interactions between the two germ layers induce the development of mesoderm.
Gastrulation and development of organ systems
Topic: Embryogenesis. Ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm are the major structures arising out of the primary germ layers. Organogenesis is the phase of embryonic development that starts at the end of gastrulation and continues until birth. During organogenesis, the three germ layers formed from gastrulation: the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm.

SoftwarePhysics May 2014
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm (the middle layer) and endoderm (the innermost layer). [1] It emerges and originates from the outer layer of germ cells. The word ectoderm comes from the Greek ektos meaning "outside", and.

Ectoderm, Endoderm, & Mesoderm YouTube
Gastrulation leads to three germ layers—ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm—that are separated by two basement membranes. In the mouse embryo, the emergent gut endoderm results from the widespread.

Pin on біологія
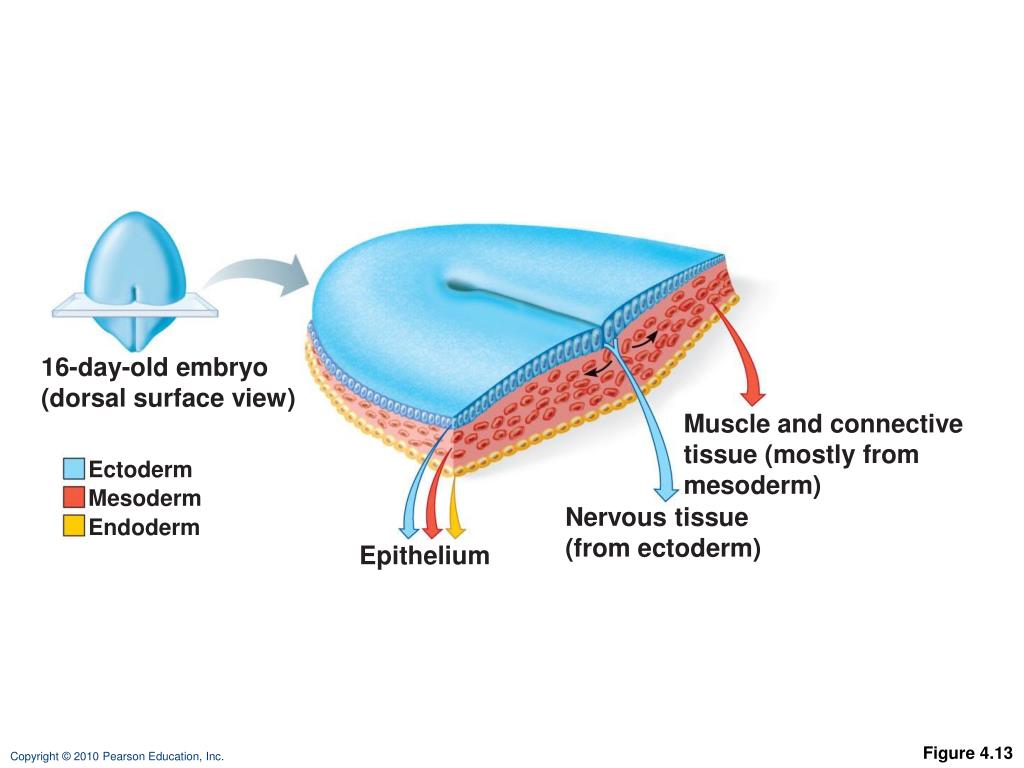
In human embryology, weeks six through eight are characterized by the growth and differentiation of tissues into organs. This process is known as organogenesis and occurs from weeks three through eight; the embryonic period. During week three, the process of gastrulation occurs, which establishes three distinct cell layers; the mesoderm, endoderm, and ectoderm. These are the primary germ cell.

Major Structures Arising Out Of Primary Germ Layers Embryogenesis MCAT Content
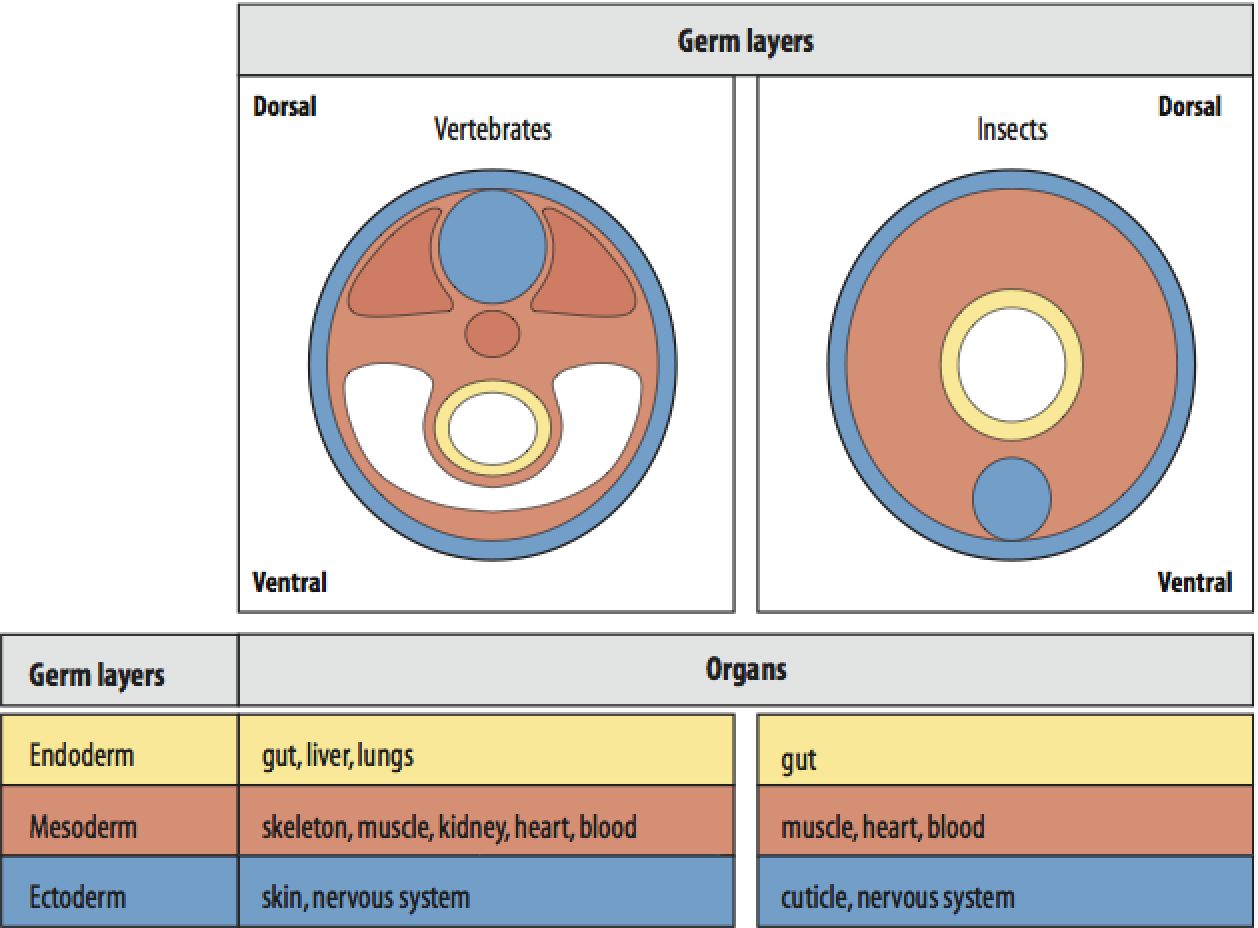
The mesoderm germ layer forms in the embryos of triploblastic animals. During gastrulation, some of the cells migrating inward contribute to the mesoderm, an additional layer between the endoderm and the ectoderm. The formation of a mesoderm leads to the development of a coelom. Organs formed inside a coelom can freely move, grow, and develop.

How are the three germ layers formed?
Formation of the three primary germ layers, ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm, is an early distinction between groups of cells in developing embryos. Our understanding of their generation in vertebrates has benefitted from the classical experiments of Nieuwkoop and his colleagues (referenced in Nieuwkoop, 1997), in which explants of tissue from the animal hemisphere of amphibian embryos (fated.

28.2 Embryonic Development Anatomy & Physiology
The CNS system involves 3 germinal layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. The ectoderm is the key initiating player in the embryogenesis of the CNS. The ectoderm is further sub-specialized as the (1) surface ectoderm, which differentiates into the epidermis, nails, and hair. The ectoderm is also sub-specialized to form the (2) neural.

Growth and Development Pocket Dentistry
The gastrointestinal (GI) system involves three germinal layers: mesoderm, endoderm, ectoderm. Mesoderm gives rise to the connective tissue, including the wall of the gut tube and the smooth muscle. Endoderm is the source of the epithelial lining of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, gallbladder, pancreas.

BIOLOGY FORM 6 EMBRYOLOGY
The process of gastrulation generates the three primary germ layers ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm. Gastrulation primes the system for organogenesis and is one of the most critical steps of development. The endoderm is the innermost layer, which gives rise to the gastrointestinal tract, the lining of the gut, the liver, the pancreas, and.
PPT 4 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3070951
The entire nervous system forms via the process called neurulation in which neural tube and neural crest form initially. In the third week of embryogenesis, three germ layers arise, namely, ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm, through the process of gastrulation. The overlying ectoderm is induced and thickened by the notochord and the neural plate forms. The neural plate then gives rise to the.
Introduction to ectoderm
Endoderm is the innermost of the three primary germ layers in the very early embryo.The other two layers are the ectoderm (outside layer) and mesoderm (middle layer). Cells migrating inward along the archenteron form the inner layer of the gastrula, which develops into the endoderm.. The endoderm consists at first of flattened cells, which subsequently become columnar.
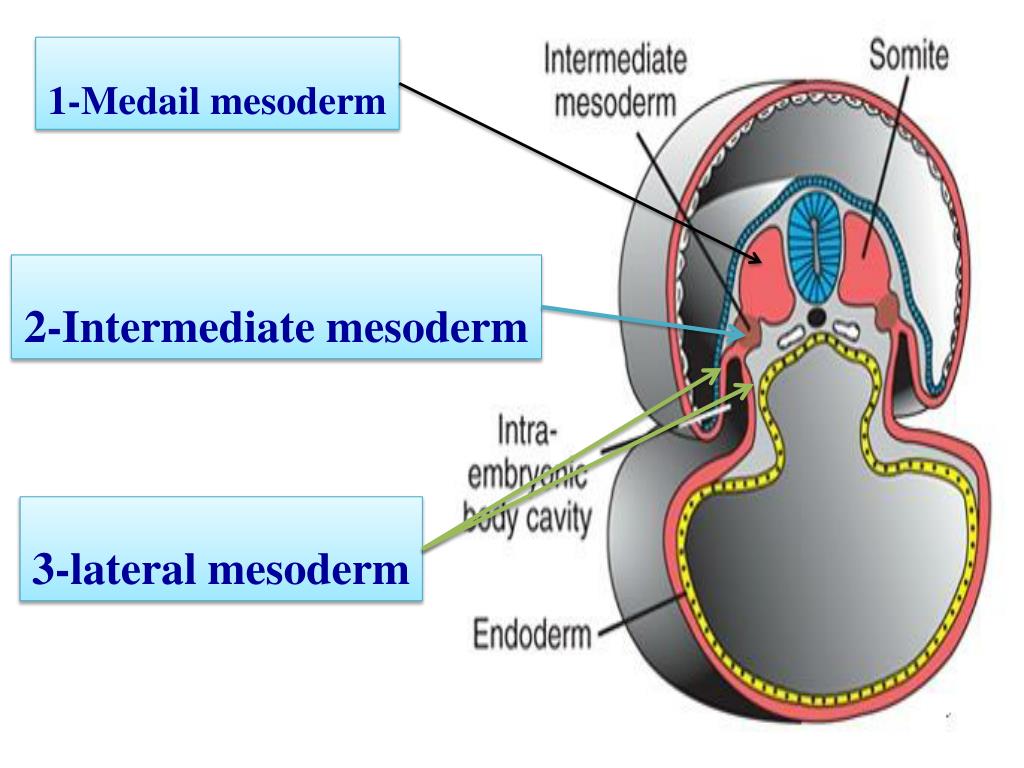
PPT Derivatives of the ectodermal germ layer PowerPoint Presentation ID1981616
Mesoderm, the middle of the three germ layers, or masses of cells (lying between the ectoderm and endoderm), which appears early in the development of an animal embryo. In vertebrates it subsequently gives rise to muscle, connective tissue, cartilage, bone, notochord, blood, bone marrow, lymphoid